Vital Information
There are four main forms of intellectual property protection relevant to products:

- Patent – this protects the functionality of a product

- Registered Design – this protects the appearance of a product

- Trade mark – this protects the branding of a product, company or business

- Copyright – this predominantly protects ‘works of art’ or audio or written material and also applies to some software and computer programs
What you need to know:
Patents
A patent protects the idea behind a product: such as HOW it works, WHAT it does and WHY it has certain features. Patents can be extremely valuable assets.
In order to be deemed worth the protection of a granted patent an invention must be:
- Novel
- Inventive
…and fit into one of the following categories:
- A new idea
- An improvement upon an existing idea
- A new combination of existing ideas
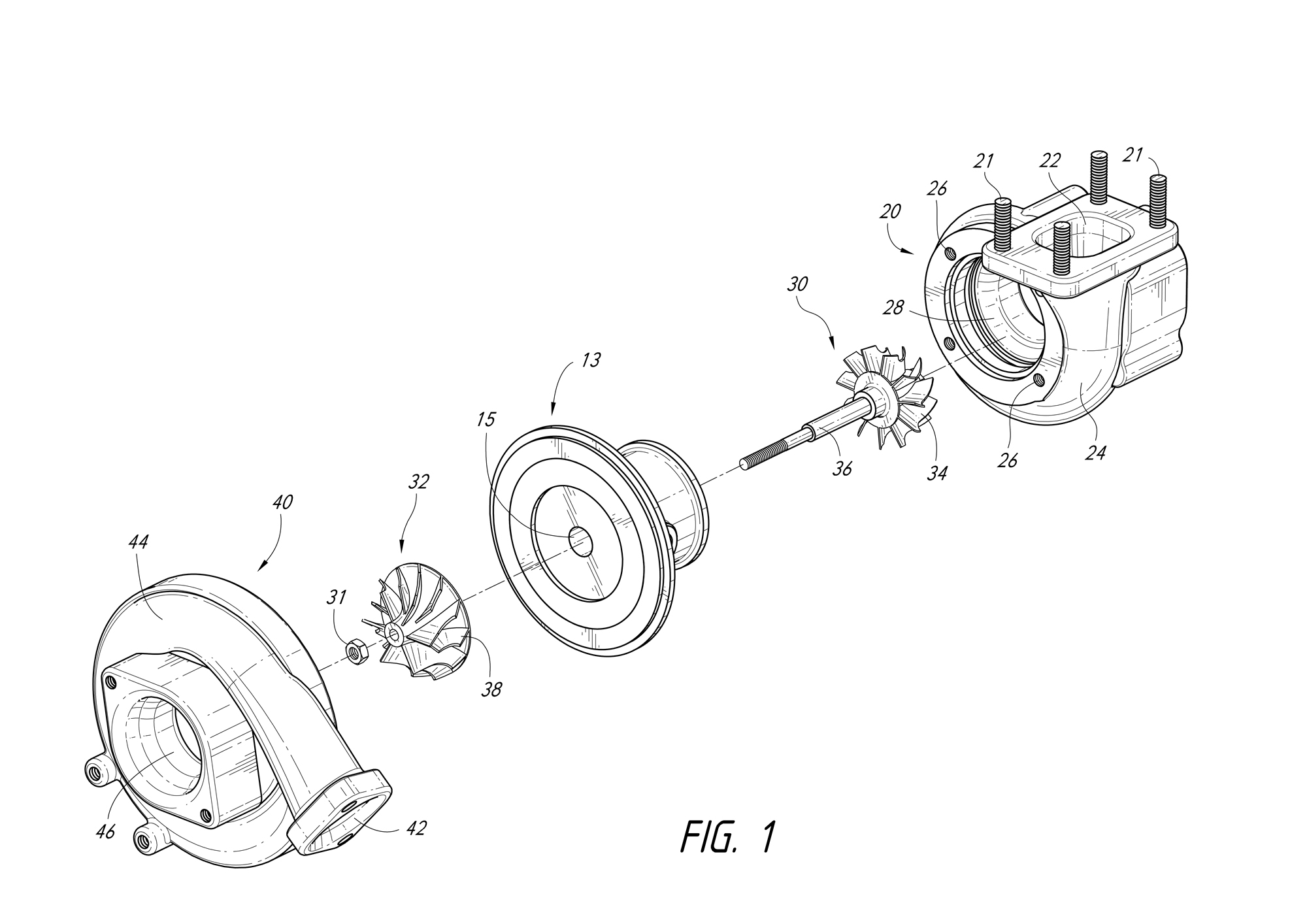
Patent applications can take up to 4½ years to be granted but as soon as you have filed your patent application you have a date you can use to show you had idea first (see ‘Patent Pending’ below!).
Granted Patents give protection against others for up to 20 years from filing the application, provided you maintain the renewal fees which keep the granted patent in force (in the UK paid annually from 4 years).
Granted Patents stop others using your idea in the country where your patent is granted and in force.
There is no such thing as a worldwide patent but there are ways of making a single application (such as the PCT application) that can be used in multiple countries.
PCT Patents & the European Patent Convention
The most far reaching application you can obtain is through something called the PCT (Patent Cooperation Treaty) which provides a single application method for around 160 countries. Other applications include the EPC (European Patent Convention) covering the majority of Europe. These types of applications are expensive however you have 12 months from your first filing to extend protection through them or into other countries.
Patent law varies from country to country so it is important to see a patent attorney when applying outside the UK to make sure you are applying correctly.
For example in America, what the UK know to be a patent would be referred to as a ‘utility patent’. Other countries have other systems like cheap short-term patents called ‘utility models’.
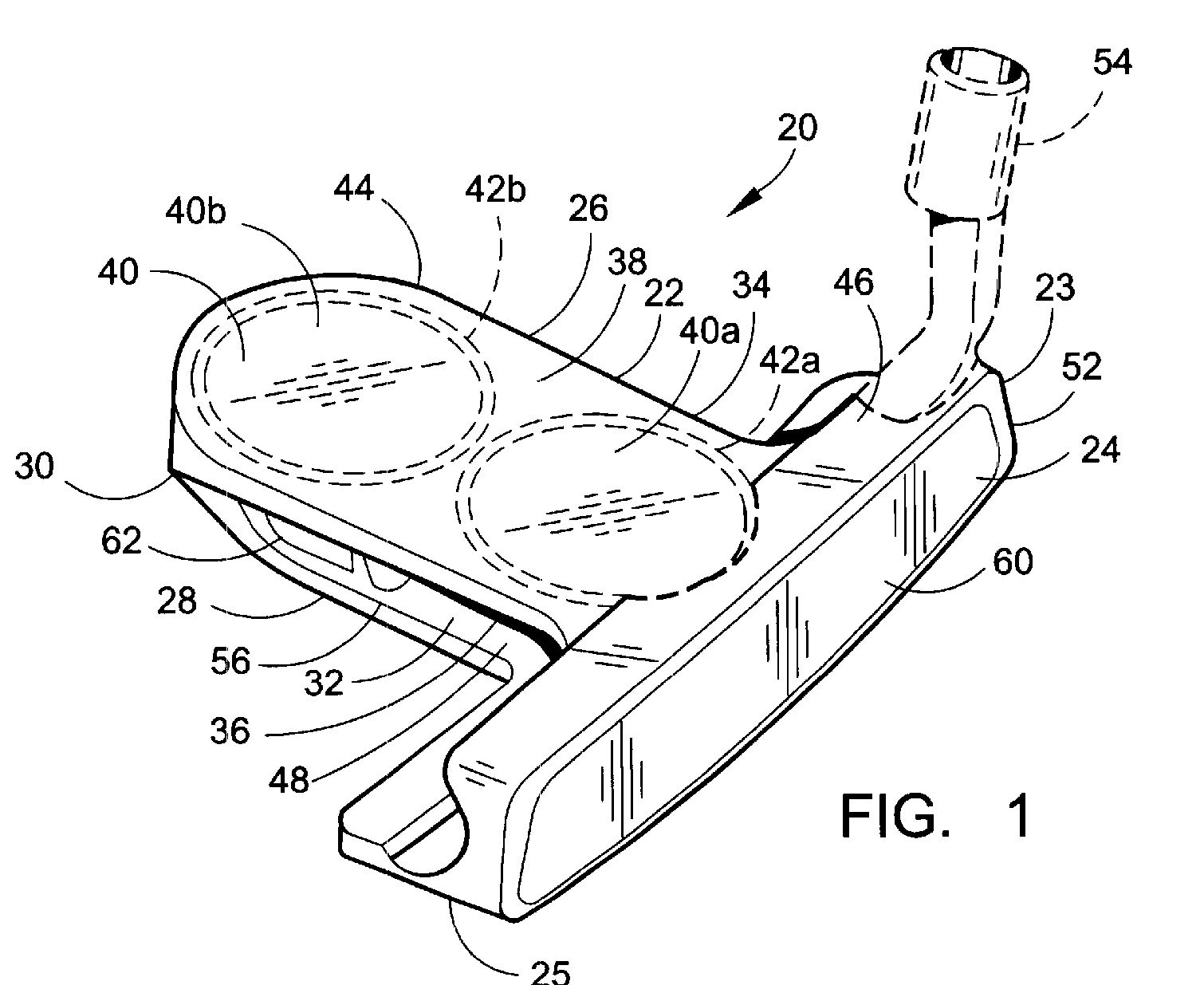
America allows business method patents, and software patents which are typically not allowed in the UK.
You cannot patent certain types of invention, including:
- literary, dramatic, musical or artistic works
- a way of doing business, playing a game or thinking
- a method of medical treatment or diagnosis
- a discovery, scientific theory or mathematical method
- the way information is presented
- some computer programs or mobile apps
- ‘essentially biological’ processes like crossing-breeding plants, and plant or animal varieties
Registered Design
A registered design protects the external shape and design of a product and this can be extended to include: lines, contours, colours, shape, texture, materials and the ornamentation.
Registered designs can also be applied for to protect patterns
Registered designs in Europe cover 28 countries and need to have ‘novelty’ and ‘individual character’. The application is not examined and is generally considered as of lower value than a patent.
You can find more information on Registered designs here.


European registered designs provide protection on your design for up to 25 years, with 5 year renewal periods.
In the USA, protection of designs is through Design Patents, which are much more expensive to apply for.
There is an International Registration of Industrial Designs known as the Hague Agreement, but this is expensive, only covers a selection of countries and does not include some of the major markets.
Trade mark / Trademark
Trade marks protect logos, symbols or names of products or businesses. It is possible to have unregistered trade marks (protected by ‘passing off’) or registered trade marks.
Trade marks can have appeared in the public domain for any length of time before registering and therefore do not have to be 'new' - but if someone else is already using the trade mark you may have trouble trying to claim it as your own if you leave it too late.
Trade marks may not be capable of registration if they describe the product for which they are used, i.e. 'Good Wine'
Trade marks must be filed in each different country and last indefinitely if renewed. In the UK this must be every 10 years.


Similar to designs it is also possible to register trade marks in Europe. A so-called CTM gives the owner protection for all 28 EU Member States in a single registration as of July 2014.
Also similar to registered designs, the ‘Madrid system’ is a centralised international system to register your mark in up to 92 countries.
The symbol TM can be used against unregistered trade marks. The symbol ® can only be used for registered trade marks.
More information on Trade marks here.
Copyright Protection
Copyright automatically applies to any original ‘work of art’ - literature, manuscript, artwork, music, oral, audio or recording.
Computer programs, databases and websites can also be protected by copyright.
Copyright is an automatic right and does not require any formal form of registration to be applied to your work.
Copyright relates to the work of art, not to concepts or ideas affiliated with the work. For example the copyright protection on the book Lord of the Rings does not prohibit the re-use of plots or storylines relating to Hobbits/infinite power-bearing rings etc. but just the physical written work i.e. the particular words in that particular order.
More than one form of copyright may exist in any work of art, for example for the Lord of the Rings book, the cover art, the layout of the type, the pictures etc. – and may be owned by many different owners.
Copyright protection stops others from copying, adapting, distributing, renting or performing that particular work without prior permission from the author.


For most articles, Copyright lasts until 70 years after the death of the author.
For films, Copyright protection lasts until 70 years after the death of the last surviving director, author of film script or composer of the music specially created for the film.
Generally speaking, material created in the UK will also be protected overseas, due to the UK's membership of several international conventions.
Although automatic, generally speaking it is sensible to put the © symbol on any material you wish to protect.
